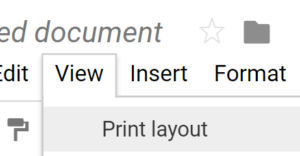
In this day in age, we don’t need to print as much as we used to. While Google Docs will allow you to print pages of content, sometimes you just want to use it as a digital document to keep notes and pictures that you’ll never print. When you insert pictures into a Google Doc, due to their size, you’ll often find that they move onto the next sheet leaving a large white space before. This is annoying but easily solved by making it appear as if you were working with one page / sheet of unlimited length. In Google Docs, just uncheck the Print Layout under the View menu.
Category: Web Development
Using JavaScript to Temporarily Prevent Clicks and Form Submissions
When you test interactivity of a web page by clicking a link or submitting a form, you sometimes don’t want to be redirected to a new page. Using JavaScript in your browser’s console, you can easily make this happen.
- Open your browser’s inspector and inspect the element (link or button) that when clicked on, won’t take you to a new page
- In your browser’s console, add the following JS
$0.addEventListener("click", function(e) {
e.preventDefault();
});
How to F*$%-ing Hide Content in HTML Emails in Outlook on Windows!
Here’s how you f*$%-ing do it! Just wrap the content you want to f*$%-ing hide in this client-specific conditional.
<!--[if !mso 9]><!-->
This will not appear in Outlook on Windows.
<!--<![endif]-->Since you’re probably using HTML tables to structure your emails, and you’re probably using CSS classes to hide and show different duplicate content for desktop and mobile, your code will probably look something like this:
<style>
.showOnMobile {
display: none;
overflow:hidden;
}
@media screen and (max-width:684px) {
.showOnMobile {
display: block !important;
}
}
</style><!--[if !mso 9]><!-->
<td class="showOnMobile">
This will not appear in Outlook on Windows.
</td>
<!--<![endif]-->
There you have it. Now go and do something useful with your time instead of f*$%-ing around with HTML emails all f*$%-ing day long!
Use PHP’s Built-in Web Server for Quick, Local Development
I recently need to build a simple PHP script but I didn’t feel like spending a lot of time configuring a web server, e.g. Apache. and having it support PHP. It turns out that PHP has its own built-in server and it’s super easy to use. Here are the steps:
- Download PHP
If you’re on Windows, which I was at home, then go to https://windows.php.net/ and download a pre-compiled PHP binary. I chose the latest x64 NTS (non thread safe) zipped version. - Unzip the archive
e.g. to c:/Program Files/PHP/ - Open a terminal window
We start and stop the server from the command line - Go to your project folder
e.g. cd c:/Documents/Projects/mysite - Start the server
If PHP is on your path, then you can just do
php -S localhost:8000
otherwise, you’ll need to specify the full path to PHP, e.g.
c:/Programs/PHP/php -S localhost:8000 - View your PHP site
Go to localhost:8000 in a web browser and see your site, e.g. index.php - Stop the server
Press Ctrl-C to quit
If you want to start the server in a particular document root directory, e.g. c:/Downloads/foo, you can do
php -S localhost:8000 -t c:/Downloads/foo
View the PHP built-in server documentation
cd C:\Users\abdul\Documents\Projects\zabuun.com
C:\Users\abdul\Documents\Projects\zabuun.com>”C:/Program Files/PHP/php” -S localhost:8001
Working with GitHub and Git Using the Command Line
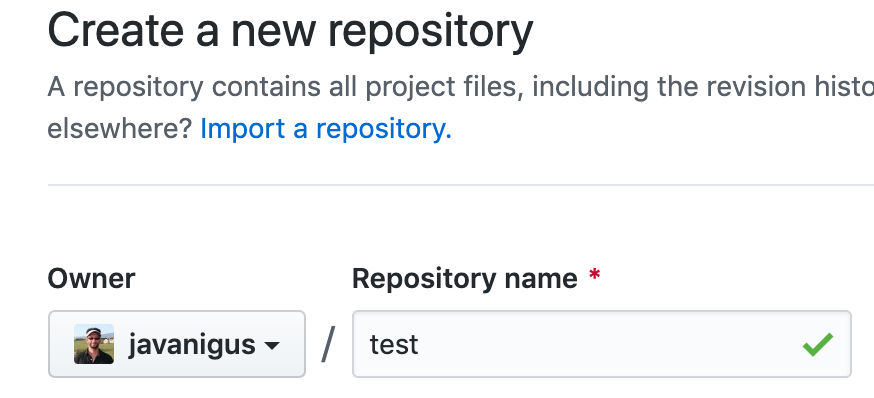
Create a repo called “test” in GitHub
Create a new repo in GitHub called “test” and check the checkbox to initialize it with a README.md file.
This repo called “test” will contain a default branch called “master”. On your local machine, this GitHub repo is called “origin” by default because it is the repo you “originally” cloned from. The “master” branch is usually used for production. Together, this repo and branch are referred to as “origin/master” (remote name / branch name).
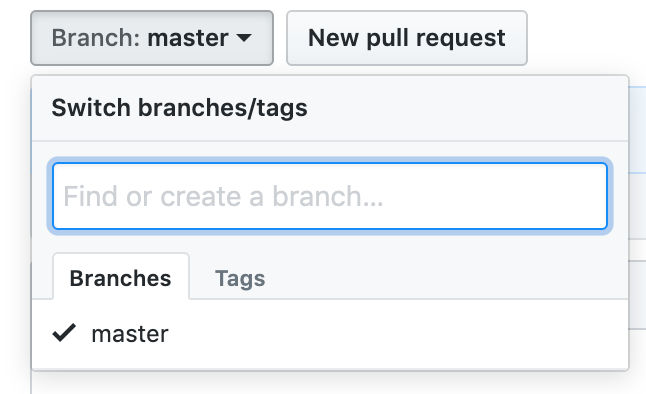
Create a “develop” branch in GitHub
If you need a separate branch for development, you can create it and call it “develop”. If you create this branch in the “test” repo on GitHub, it will be called “origin/develop”.
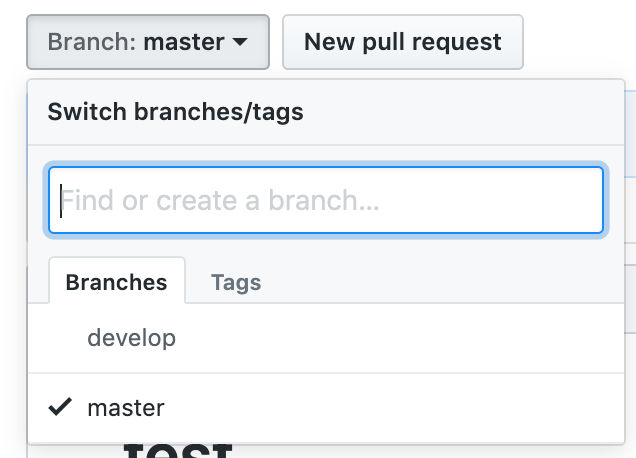
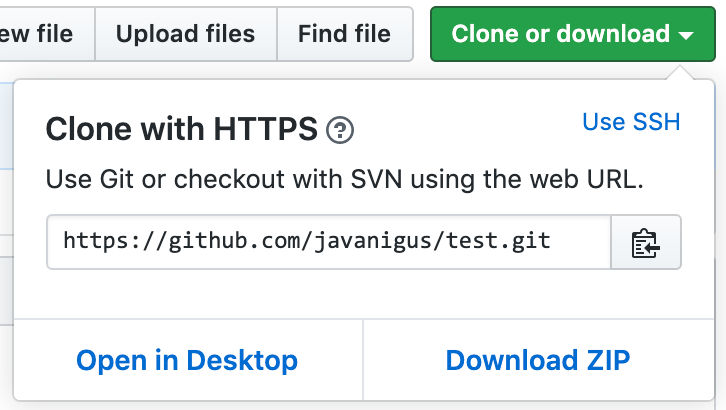
Get GitHub clone URL
In GitHub, get the URL to clone the repo, e.g. https://github.com/javanigus/test.git
Go to local projects folder
On your locale machine, go to a folder where you want this project to exist, e.g. /Users/ayahya/Projects/
cd /Users/ayahya/Projects/
Clone the remote repo on GitHub to your local machine
git clone https://github.com/javanigus/test.git
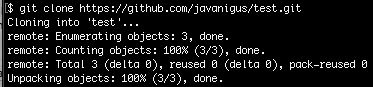
This will create a folder that is the name of the repo, e.g. “test”
Go to the repo folder
cd test
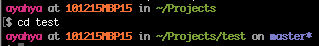
Since it says “master*”, then the files within it are set up to track remote branch “master” from origin.
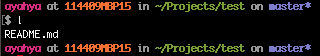
See what’s in the repo folder
Using the “ls” command, we see the same, one file (README.md) that is in GitHub.
See the log
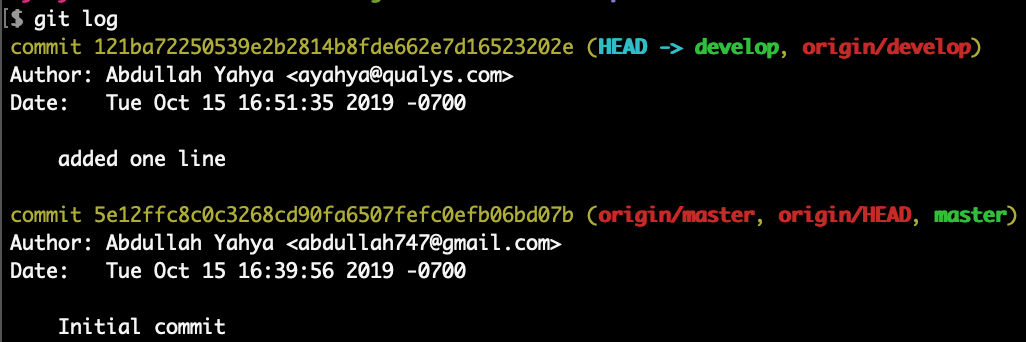
git log
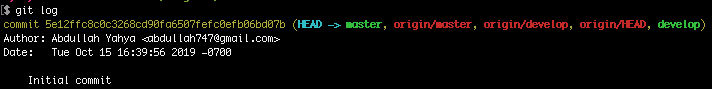
HEAD is a reference or pointer to the last commit in the currently checked-out branch (master). Notice that origin/master (remote) and origin/develop (remote) and local master and local develop are in sync because they are listed on the same line.
List remote repos
git remote
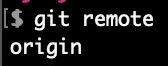
We see that we only have one remote repo called “origin”.
Switch to the develop branch
git checkout develop
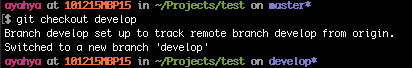
Since it says “develop*”, then the files within it are set up to track remote branch “develop” from origin.
List all branches
git branch
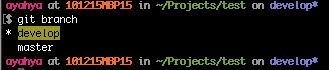
Since there is a * beside “develop” and it is highlighted, the local files are set to track remote branch “develop” from origin.
Open the project in a text editor and edit a file
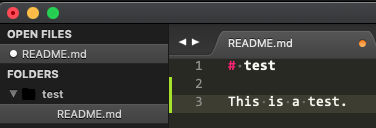
In this case, I added the text on line 3.
View the status of your local files
git status
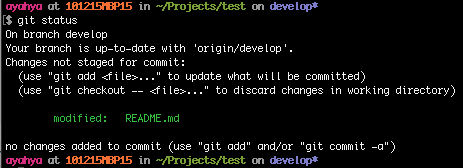
The README.md file has been modified.
Undo (revert) the modification
git checkout - README.md

View the status of your local files
git status
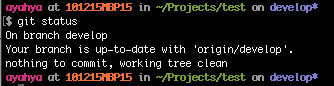
The local branch is up to date with origin/develop on GitHub.
Redo the modification
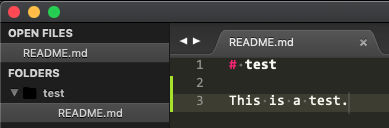
View the status of your local files
git status

Stage (add) the modified file so it can be committed
git add README.md
or
git add .
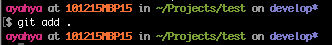
View the status of your local files
git status
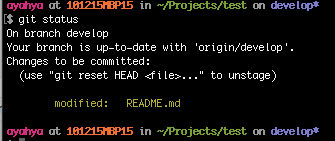
Unstage the modified file
git reset HEAD README.md
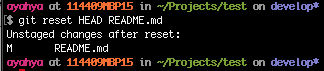
Check the status of the files
git status
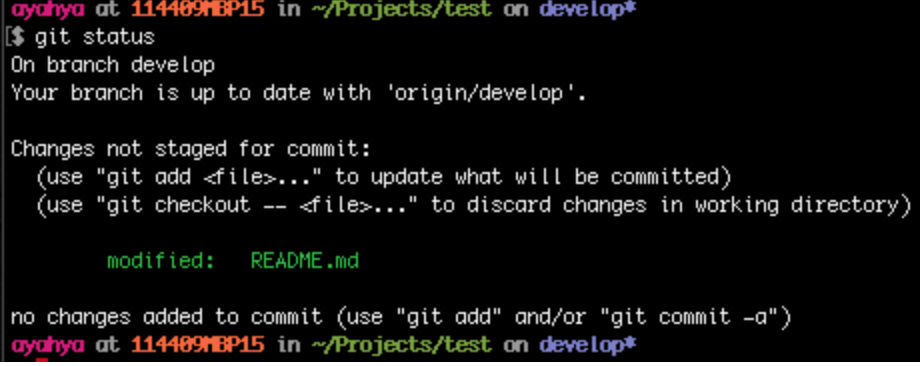
Restage (re-add) the modified file so it can be committed
git add README.md
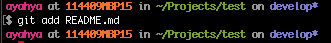
Commit the modified file
git commit -m "added one line"
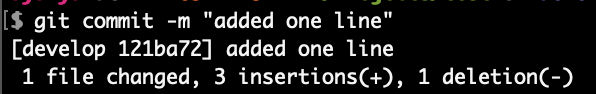
View the status of your local files
git status

Now, the local “develop” branch is ahead of the remote “develop” branch (origin/develop) by 1 commit. Also, there is nothing else to commit and the working tree is clean.
Check the log
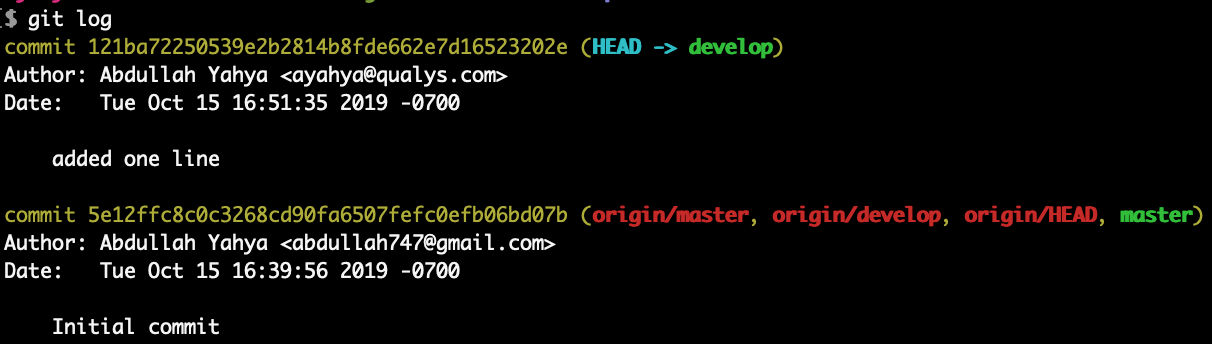
This shows that local “develop” branch is ahead of local “master” branch, remote “master” and remote “develop” by 1 commit.
Push local changes to remote
We’ll push local branch “develop” to origin/develop on GitHub.
git push origin develop
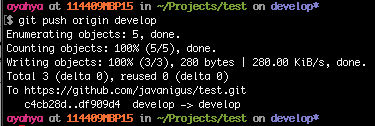
On GitHub, in the “develop” branch, you’ll see the added line.
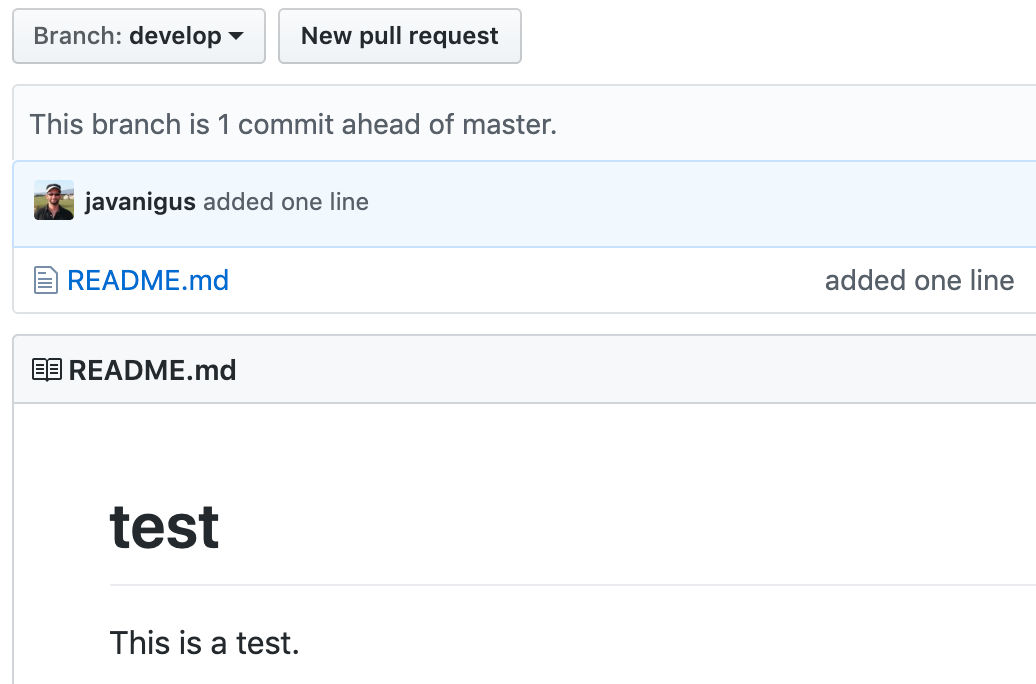
Check the log
Now we see that both local and remote “develop” branches are in sync and ahead of local and remote “master” branches by 1 commit.
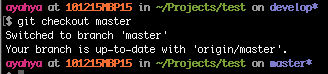
Switch to master branch
git checkout master
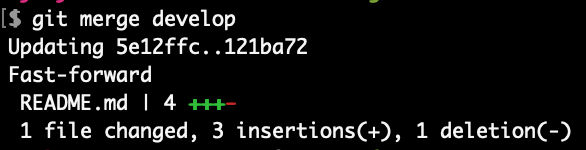
Merge changes from “develop” to “master”
The local “master” branch doesn’t have the changes in “develop”. Let’s merge the changes from the local “develop” branch into the local “master” branch.
git merge develop
View the status of your local files
git status
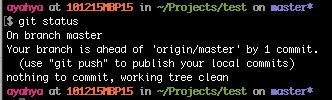
The local “master” branch is now ahead of the remote “master” branch (origin/master) by 1 commit.
See the log
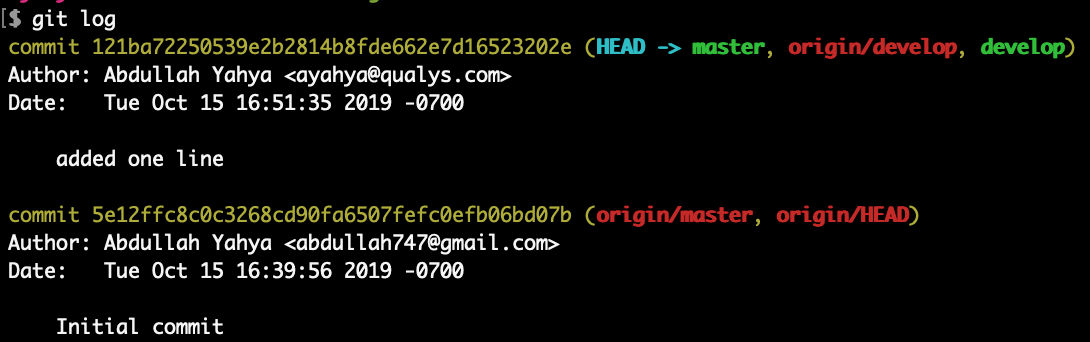
Now we see that local “master”, local “develop”, and remote “develop” are in sync and ahead of remote “master” by 1 commit.
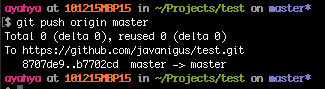
Push local changes from remote
We’ll push local branch “master” to origin/master on GitHub.
git push origin master
View the status of your local files
git status
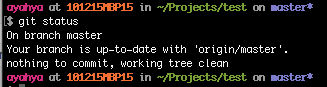
The local branch is now up-to-date with origin/master on GitHub.
On GitHub, in the “master” working tree you’ll see the added line.
Check the log
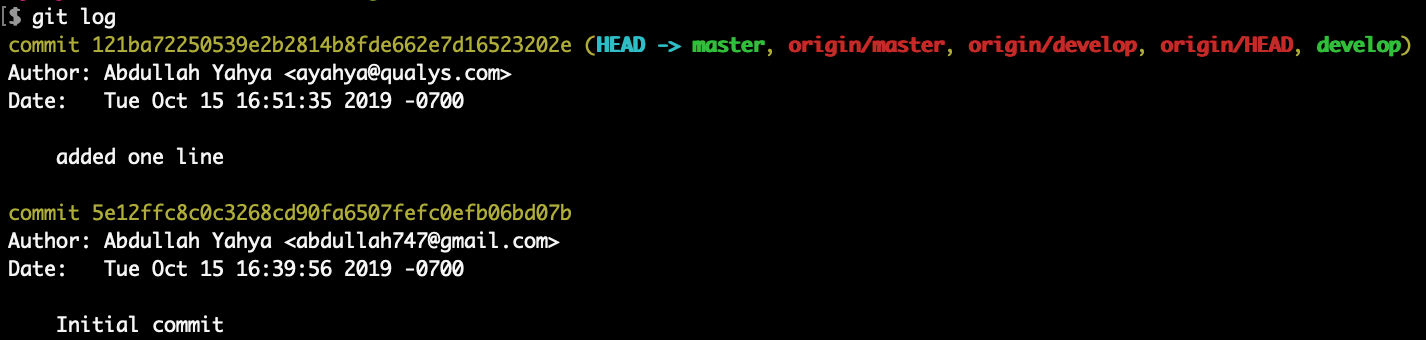
Now all branches, local and remote, are in sync.
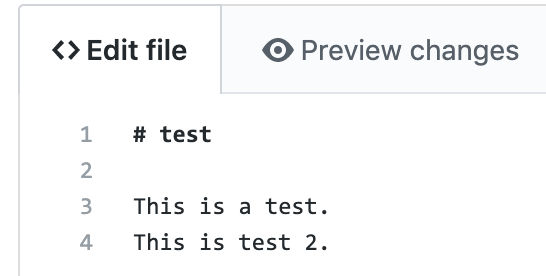
Make a change on origin/master and commit it
In this case, I added line 4.
Check status of local “master” branch
git status
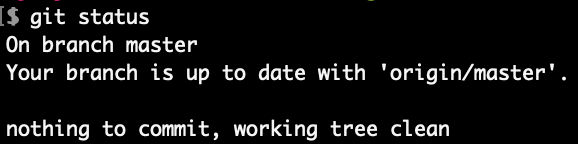
We see that our local “master” branch is in sync with remote “master” branch even though we just committed a change in remote “master”.
Fetch updates from remote repo
In order to see what has changed remotely, run git fetch.
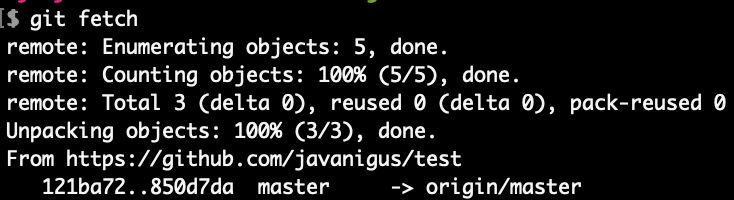
Check status of local “master” branch
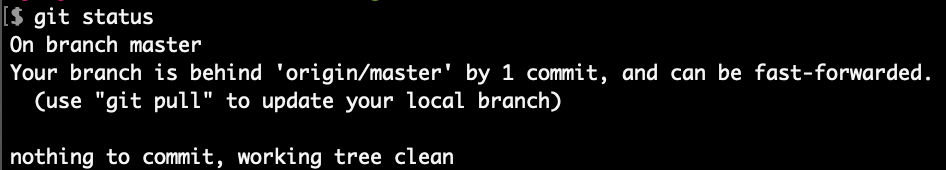
Now, we correctly see that our local “master” branch is behind the remote “master” branch (origin/master) by one commit.
Pull changes from GitHub (origin/master) down to local “master”
git pull
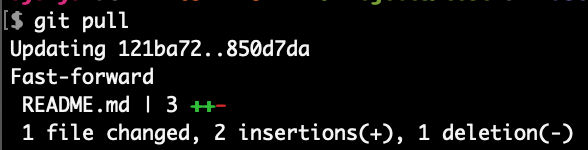
Check status of local “master” branch
git status
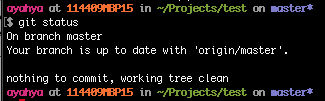
Local and remote “master” branches are in sync again.
Check the log
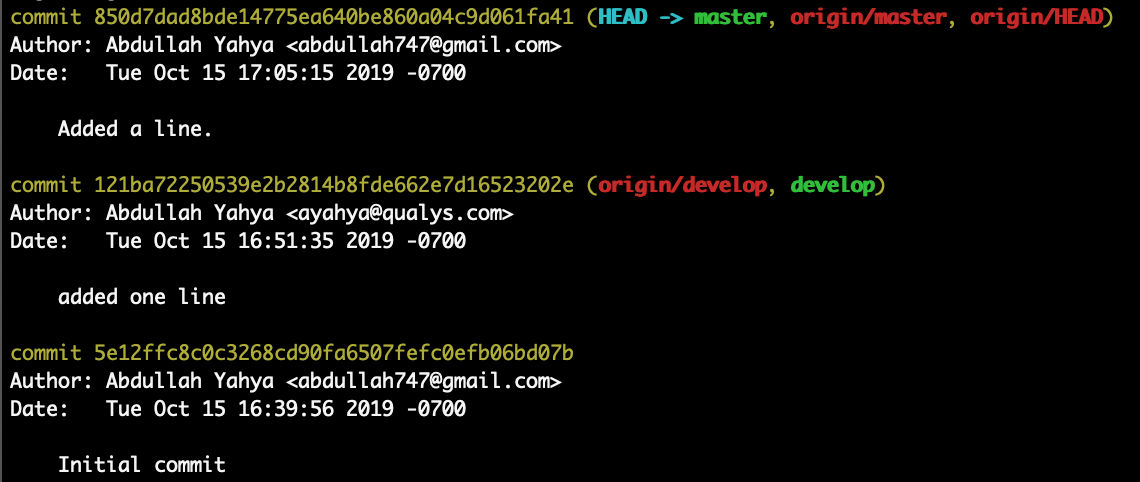
Now we see that local and remote “master” branches are ahead of local and remote “develop” by 1 commit.
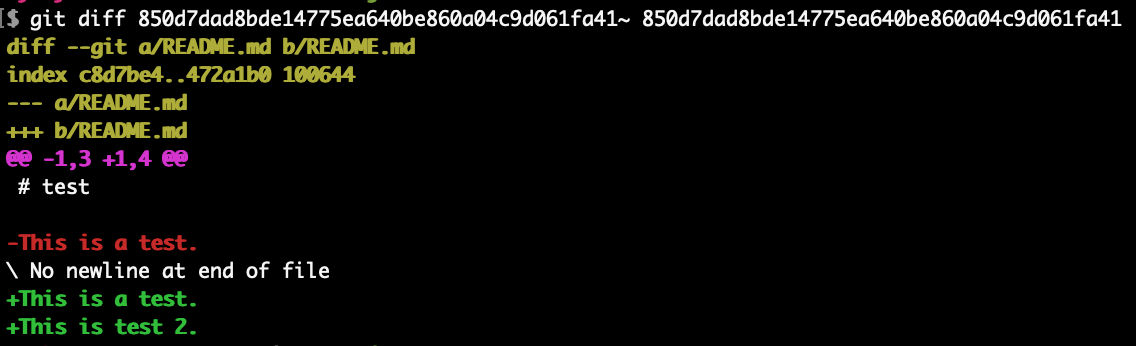
See what changed
To see a change in a particular commit, run git diff on the commit, e.g. to see the most recent change (commit 850d7dad8bde14775ea640be860a04c9d061fa41), we run
git diff 850d7dad8bde14775ea640be860a04c9d061fa41~ 850d7dad8bde14775ea640be860a04c9d061fa41
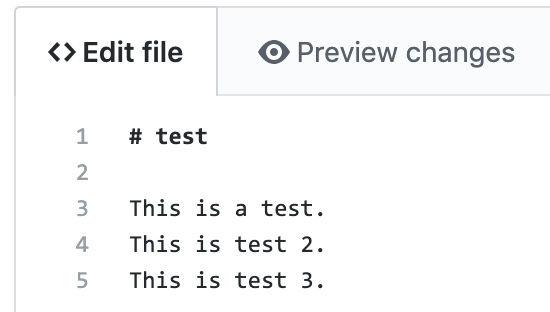
Make another change on origin/master and commit it
This time I added line 5.
Fetch changes and check status
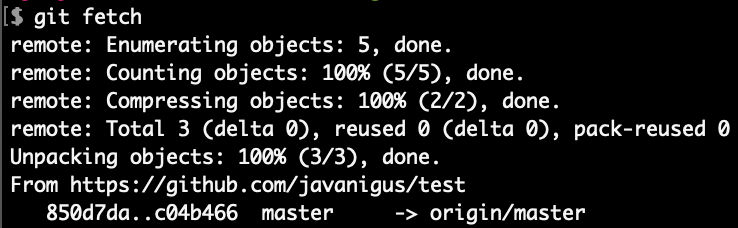
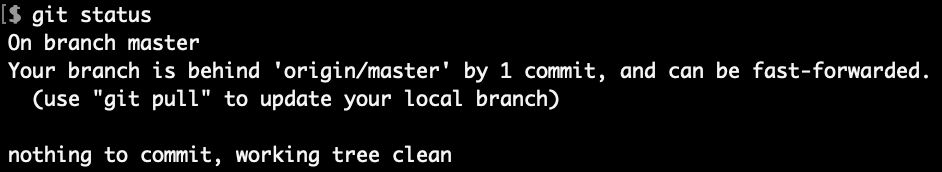
We see that local “master” is behind remote “master” by 1 commit, as expected.
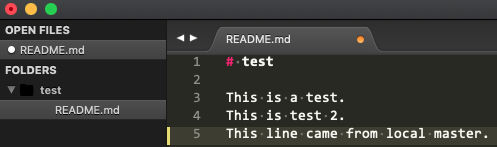
Edit local “master” and commit it BEFORE pulling changes from remote “master”
I added line 5
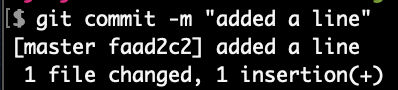
Check status
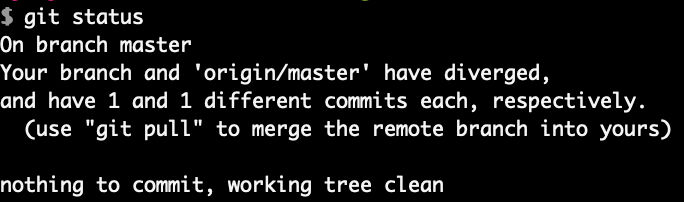
Now we see that local and remote master have each diverged because we didn’t do a pull before committing.
Run git pull to merge remote “master” into local “master”
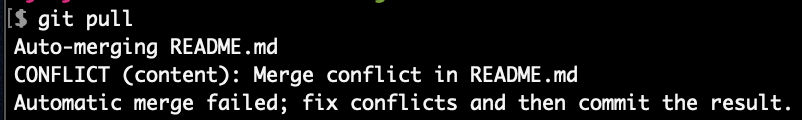
We see a conflict because the change in remote “master” and local “master” was in the same file and on the same line (line 5).
Resolve conflicts
Open the file containing conflicts and edit it.
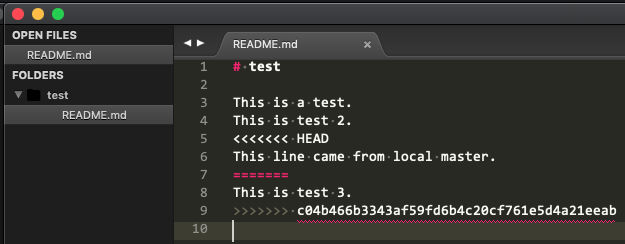
Since we want to keep both lines, just remove the conflict divider markers.
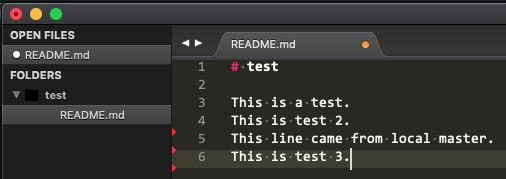
Check status
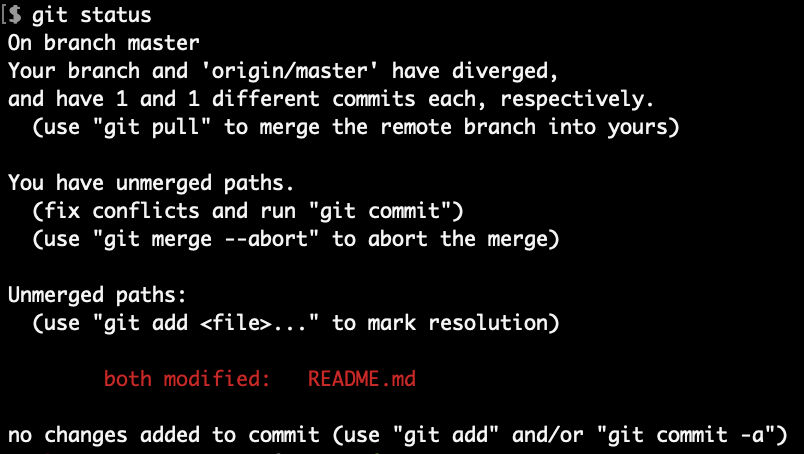
Mark conflict resolved
To mark the conflict as resolved, use “git add” and then check the status.
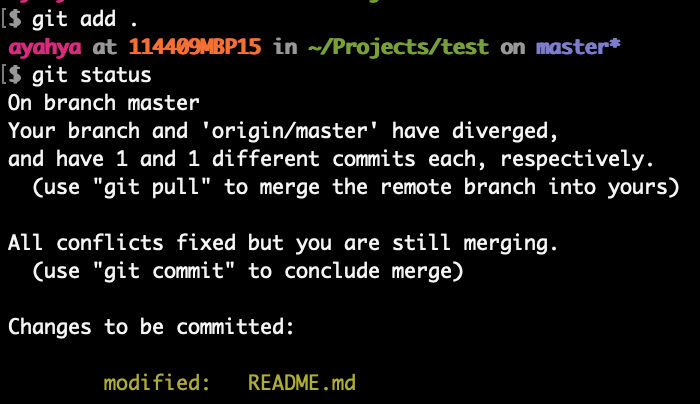
We see that the conflicts have been fixed but we are still merging.
Commit the merge

To avoid having diverged commits and pull conflicts, always do a git pull before committing.
Check status and log
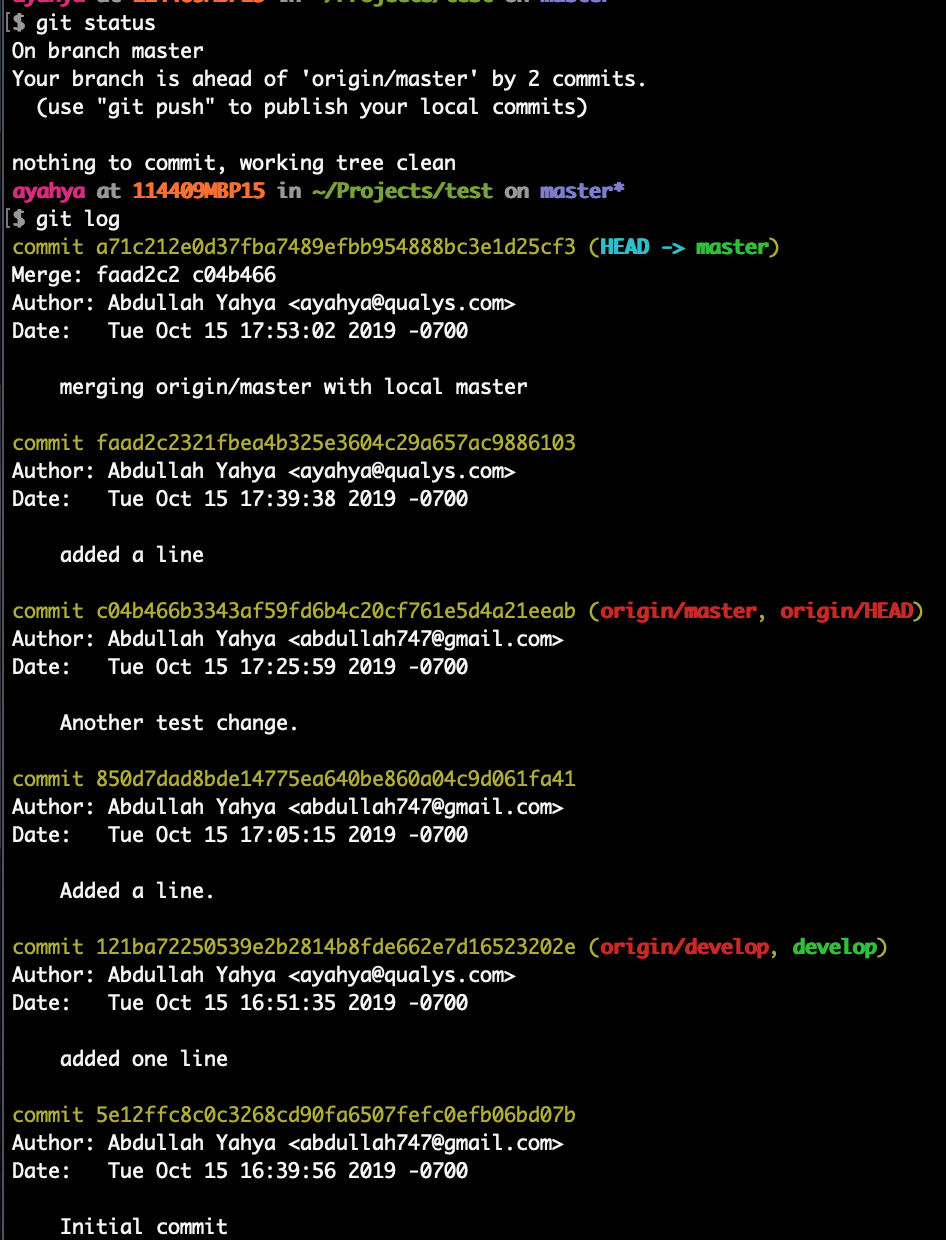
We see that
- local “master” is ahead of remote “master” by 2 commits
- local “master” is ahead of local and remote “develop” by 4 commits
- remote “master” is ahead of local and remote “develop” by 2 commits
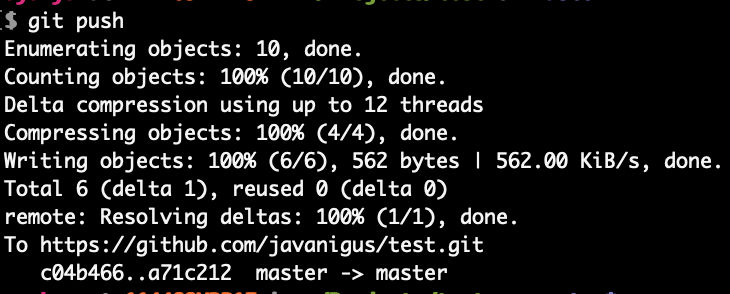
Push local changes to remote
Check log
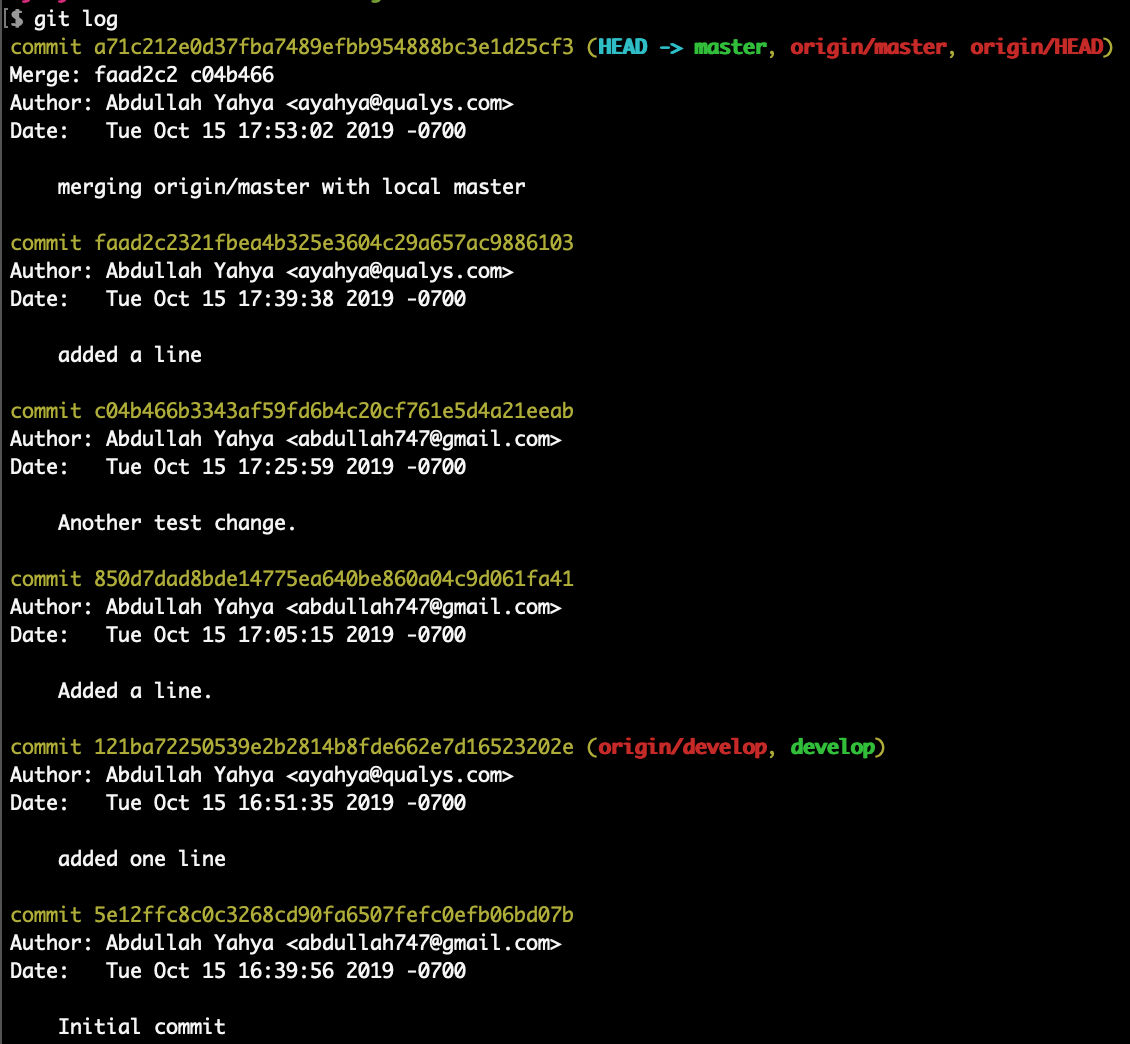
Now local and remote “master” are in sync and are ahead of local and remote “develop” by 4 commits.
Easily Add Music to Video Using Corel VideoStudio
Adding your own music or audio to a video clip is something many people like to do. Fortunately, this is very easy using Corel VideoStudio. Below are steps to add music to a video.
Insert media files, e.g. a video and an audio file
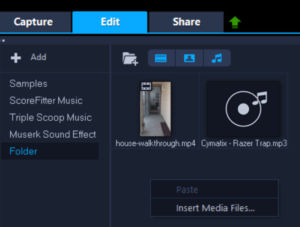 Continue reading Easily Add Music to Video Using Corel VideoStudio
Continue reading Easily Add Music to Video Using Corel VideoStudio
IrfanView for Batch Image Processing
When you’ve got a bunch of images to process, IrfanView makes the process simple and quick. Here’s an example of how to
- auto trim / remove whitespace
- resize images
- optimize JPGs
Open IrfanView and do the following:
- File > Batch Conversion / Rename
- Work As: check “Batch Conversions”
- Look In: Browse to the folder containing all of the images then click “Add All”
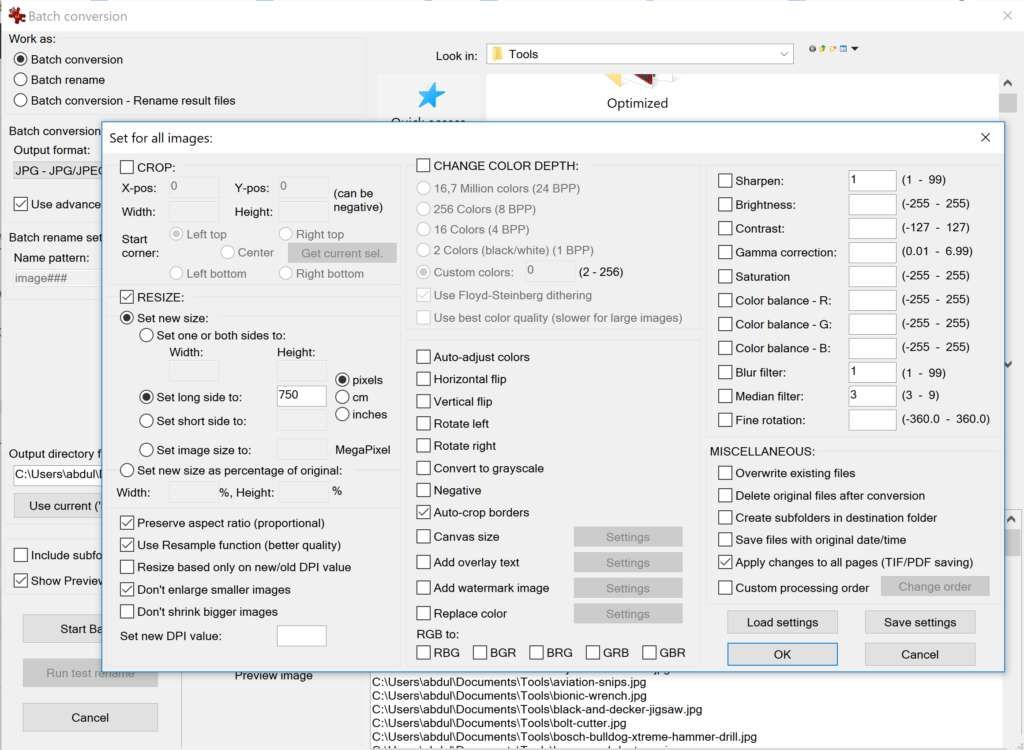
- Batch Conversion Settings: choose “JPG”, click “Options”, for “Save as quality” choose 65, check “Save as progressive JPG”
- Batch Conversion Settings: click “Advanced”,
- check “Auto crop borders”
- check “RESIZE”, check “Set new size”, for “Set new size to” enter “750” pixels, check “Don’t enlarge smaller images”
- Output Directory: create and choose a different directory, e.g. a subfolder called “processed”
- Click “Start Batch”
Easily Create Curved Arrows on Mac Using Preview
When you need to annotate a document and explain certain parts of it, using arrows can be very helpful. If you’re on a Mac, adding arrows, both straight and curvy, is very easy using the Preview application. Here’s how to do it
- Open an image in Preview
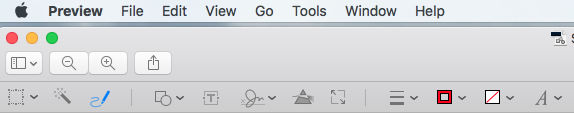
- Open the Toolbar (View > Show Toolbar)
- Click on the “Sketch” icon (3rd from the left) so that it’s highlighted blue
- Choose a line thickness
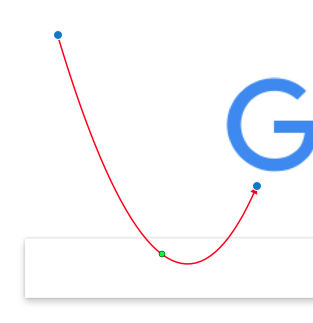
- Click and drag to create a curved line with an arrow just as you would with a pen without lifting the pen. This will result in a curved arrow.
- If the curvature doesn’t look right, adjust it by moving the 3 control points.
- Then add some text by clicking on the text tool (last icon with the letter A)
You can also create straight lines by drawing a line. Preview will detect that you are trying to draw a line and make it straight for you.
LiveWeave: An Online HTML, CSS, JS Editor with Live Preview and Handy Tools
If you’re looking for a simple and handy online HTML, CSS and JS playground, you might light LiveWeave. You don’t have to create an account to get started and the UI is pretty polished.
Continue reading LiveWeave: An Online HTML, CSS, JS Editor with Live Preview and Handy Tools